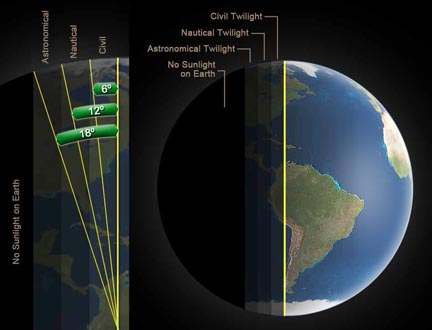
Sun's Position Over Earth
(to update, reload page)
Courtesy:
Fourmilab Switzerland
View Earth's Night Half
Day, Night & the Analemma
Earth Tilt, Sunrise & Sunset
Six Current Views of Earth
Current Global Cloud-Cover
Current Global Weather
We hope you don't sit at your computer when there's a perfectly beautiful night-sky outside to observe!
Don't forget: the tools throughout this site are intended to help you observe the real sky!
One of the best (and most fun) ways of learning the constellations is by using CELESTIA! (1.6.x) Then go view them in your sky!
Are you unfamiliar with our 1.6.x and 1.4.1 links? For an explanation click here.
WHAT CAUSES MOON PHASES
STARS
D3 Celestial Starmap awe-
some sky tool!
CONSTELLATIONS

North Circumpolar Constellations
Due to star motion, over eons Constellation Shapes Change quite dramatically!
Here are links to some sites offering good diagrams and background information on the 88 official constellations.
SEDS Constellation Pages:
Table of Constellations
Constellation Families
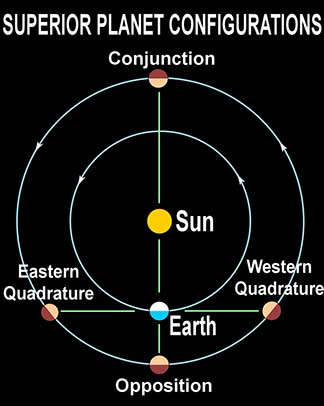
ELONGATIONS &
CONFIGURATIONS
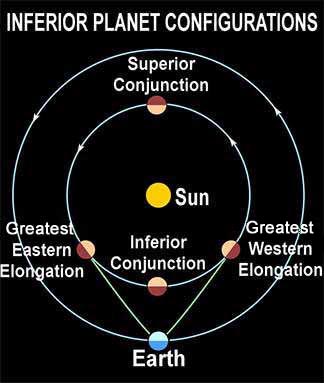
Two times each year when each Inferior Planet's orbit is seen "edge-on" from Earth:
Mercury's Venus's
Planetary Configurations Simulator
USEFUL ASTRO-WEBTOOLS
NASA:
Julian Date Converter
Coordinate Converter
Heasarc Tools
NEW HORIZONS:
Astronomical Lexicons:
NASA / JPL:
Basics of Space Flight
HubbleSite Ref. Desk
Imagine the Universe!
NED (quite extensive)
List of Constellations (with pronunciations):
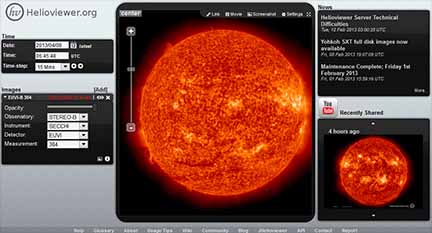
HelioViewer might just be the best free solar astronomy tool on the web, giving you access to countless actual photos of the Sun from multiple satellites! "Time-step" through photos, and save and even make movies of what you find! This free web-tool is not to be missed.
And to help get you started, here's the direct link to the HelioViewer User Guide.
Sun Activity: Today's Vids
Sunspots may not see any
at 2019-20 Solar Min ![]()
Prominences
 WARNING! It is never
WARNING! It is never
safe to look directly at the Sun with the naked eye! And looking at it—even for an instant— through either a telescope or binoculars with- out adequate safeguards can cause permanent blindness! NEVER DO IT! To learn how to safely observe the Sun, consult your local planetar- ium or observatory.
UTC: CELESTIA'S DISPLAY OF TIME
CELESTIA's clock displays Coordinated Universal Time, UTC. Click here for a brief explanation.
SKYMARVELS™ POSTERS
SKYMARVELS™
VIDEOS
Solar Eclipses:
Lunar Eclipses:

SKY VIEWING
ACTIVITIES
MAKE A PAPER MODEL OF ESO's EXTREMELY LARGE TELESCOPE
This European Southern Ob- servatory (ESO) paper model is fun and easy to make! Extremely Large Telescope
MAKE A PAPER
MODEL SUNDIAL!
CANON has a cool website that offers free downloads, including one that lets you make a cool paper model Sundial. ![]() Chart the dial's shadow throught the day—and the year! When is the shadow longest? Shortest?
Chart the dial's shadow throught the day—and the year! When is the shadow longest? Shortest?
MORE SKY VIEWING ACTIVITIES
Our Moon page contains more activities for viewing the wonders of the sky.
CELES-TIPS
These will help you enjoy this page's 1.6.x and 1.4.1 links that run events directly in CELESTIA. If you're new to the program, these tips will also help you learn to use it.
- If CELESTIA's clock is not visible at the top-right of its window, press the V key until you see it. This also turns on information text in other corners to help you keep track of aspects of the event you're viewing. Keeping an eye on CELESTIA's clock at the top-right will help you appreciate how much time is passing in each view.
- Respectively pressing the "un-shifted" L key and K key will speed up and slow down CELESTIA's flow of time by a factor of 10 in version 1.6.x and 1.4.1.
- Respectively pressing Shift+L and Shift+K will speed up and slow down CELESTIA's flow of time by a factor of 2 in version 1.6.x only.
- Pressing the J key (either shifted or "un-shifted") will reverse CELESTIA's flow of time in version 1.6.x and 1.4.1.
- You'll find more info on our Learning Center page.
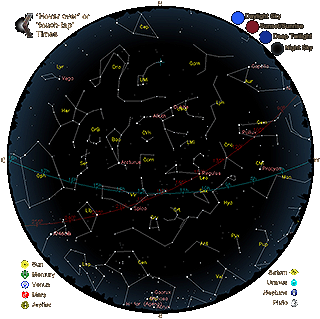

SKY VIEWING
TONIGHT'S SKY MAPS
Select the latitude closest to your own. Then click on "Get Sky Maps" and enjoy tonight's sky marvels!

Hover at bottom of map for current Earth Day & Night.
SKY VIEWING: Tonight, This Week, This Month
What's Up In Tonight's Sky
Center for Astrophysics: Current Night Sky
NASA's What's Up
NASA's What's Up: Skywatching Tips
Find your Sunrise/set and Moonrise/set times.
FOUR AWESOME ONLINE SKY MAPS:
Stellarium Web
Solar System Scope
The Sky Live
ESA's Star Mapper
2026 HIGHLIGHTS
PERSEID METEOR SHOWER
Peak: Aug 12-13 ZHR: 100
With no moon visible to hinder viewing on these nights, this year's Perseids should be AWESOME! ![]()
![]()
BEST PLANET CONJUNCTIONS:
 Feb 16 Saturn-Neptune (0.90° apart)
Feb 16 Saturn-Neptune (0.90° apart)
Mar 07 Venus-Neptune (0.07° apart)
Apr 13 Mars-Neptune (0.33° apart)
Apr 20 Mercury-Saturn (0.50° apart)
Apr 24 Venus-Uranus (0.77° apart)
Jul 04 Mars-Uranus (0.11° apart)
Aug 15 Jupiter-Mercury (0.55° apart)
MERCURY'S GREATEST ELONGATIONS:
Evening: Feb 19 18.1° E Mag: -0.2
Morning: Apr 03 27.8° W Mag: +0.5
Evening: Jun 15 24.5° E Mag: +0.7
Morning: Aug 02 19.5° W Mag: +0.4
Evening: Oct 12 25.2° E Mag: +0.2
Morning: Nov 20 19.6° W Mag: -0.3
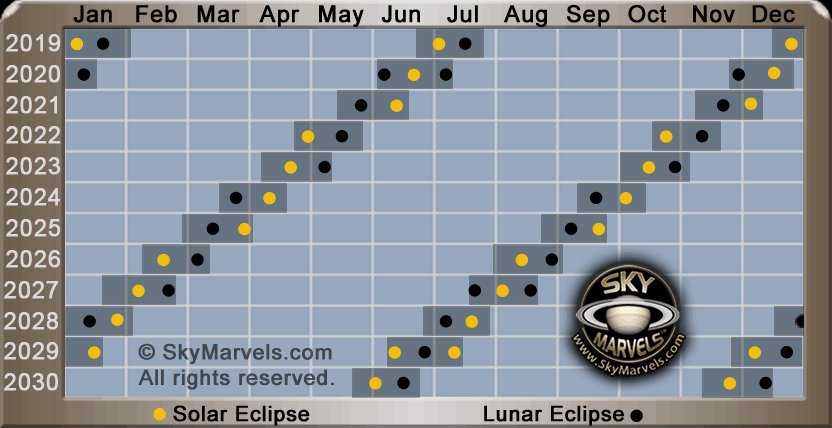
2026 ECLIPSES:
Calendar
Annular Solar: Feb 17 Total Lunar: Mar 3
Total Solar: Aug 12 Partial Lunar: Aug 28
METEOR SHOWERS: Next 12 Months
2026: Perihelion & Aphelion Equinoxes & Solstices
MOON:
![]()
Phase & Position in Phase Cycle
View with Moon Phaser interactive tool
Distance, Apparent Size and Phase from Earth
Location in the Constellations
2026 Phase List List w/ more Astronomical Events
2026 Best Moon-Planet Conjunctions
MOON PHASES 2026
video credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
MAJOR MOON PHASES: ![]()
1.
![]() New MoonsNew Moons essentially rise and set with the Sun and reflect no sunlight toward Earth. So they do not impede Deep Sky Observing all night.
New MoonsNew Moons essentially rise and set with the Sun and reflect no sunlight toward Earth. So they do not impede Deep Sky Observing all night.
2.
![]() Waxing Crescent MoonsWaxing Crescent Moons generally
Waxing Crescent MoonsWaxing Crescent Moons generally
rise between sunrise and "local
noon". Setting between sunset
and "local midnight", they are up
and impede Deep Sky Observing
early in the evening.
3.
![]() 1st Qtr Moons1st Qtr Moons generally rise near "local noon". Setting near "local midnight", they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing for the first
1st Qtr Moons1st Qtr Moons generally rise near "local noon". Setting near "local midnight", they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing for the first
half of the night.
4.
![]() Waxing Gibbous MoonsWaxing Gibbous Moons generally
Waxing Gibbous MoonsWaxing Gibbous Moons generally
rise between "local noon" and sun-
set. Setting between "local midnight"
and sunrise, they are up and
impede Deep Sky Observing from
sunset through the early morning.
5.
![]() Full MoonsFull Moons generally rise near
Full MoonsFull Moons generally rise near
sunset, then set near sunrise. So
they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing all night long.
6.
![]() Waning Gibbous MoonsWaning Gibbous Moons generally
Waning Gibbous MoonsWaning Gibbous Moons generally
rise between sunset and "local
midnight". Setting between sunrise and "local noon", they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing in the
late evening through sunrise.
7.
![]() Last Qtr MoonsLast Qtr Moons generally rise near "local midnight" and set near "local noon", allowing Deep Sky Observing only during the first half of the night.
Last Qtr MoonsLast Qtr Moons generally rise near "local midnight" and set near "local noon", allowing Deep Sky Observing only during the first half of the night.
8.
![]() Waning Crescent MoonsWaning Crescent Moons generally
Waning Crescent MoonsWaning Crescent Moons generally
rise between "local midnight" and
sunrise. Setting between "local
noon" and sunset, they are up and
impede Deep Sky Observing only during the early morning.
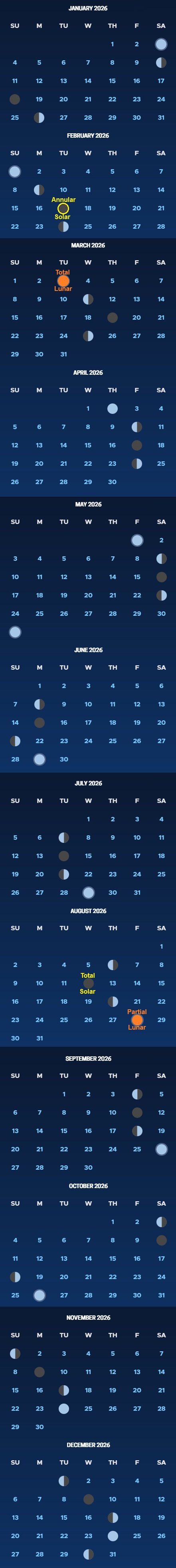
MAJOR MOON PHASES & ECLIPSES 2026
Phases shown for UTC (Coordinated Universal Time)
Also check out NASA's Daily Moon Guide
Moon Phase Interactives: #1 #2
Lunar Phase Simulator
Old Format Previous Months' Phase Calendars:
2014:
Jan
2013:
Dec
Nov
Oct
Sep
Aug
Jul
Jun
May
Apr
Mar
Feb
2026 Lunar Perigees & Apogees
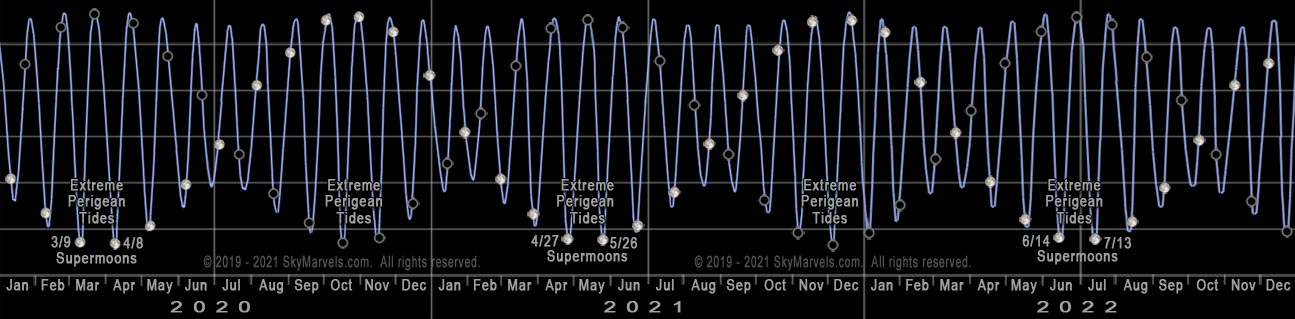
2020-2022 Supermoons & Extreme Perigean Tides
PRIOR AWESOME U.S. TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE:
2024 April 8 Maps Videos
SOLAR ECLIPSE QUICK REFERENCE MAPS
 W A R N I N G ! It is never safe to look directly at the Sun with the naked eye! Moreover, looking at it—even for an instant—through either a telescope or binoculars without adequate safeguards can cause permanent blindness! NEVER DO IT! To learn how to safely "observe" the Sun and a Solar Eclipse, consult your local planetarium or observatory.
W A R N I N G ! It is never safe to look directly at the Sun with the naked eye! Moreover, looking at it—even for an instant—through either a telescope or binoculars without adequate safeguards can cause permanent blindness! NEVER DO IT! To learn how to safely "observe" the Sun and a Solar Eclipse, consult your local planetarium or observatory.
NASA's 5 Millenia of Eclipses: Solar Lunar
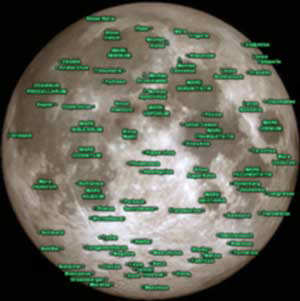
MAJOR LUNAR FEATURES
View the Moon's Features that are visible from Earth with binoculars or low-power telescope.
Download NASA's Moon Observation Journal
![]()
View and download Moon maps to aid your viewing:
USAF Lunar Earthside Map (high-res)
NASA Apollo-Era Lunar Charts:
Polar and Equatorial (small)
Moon Landing Sites
CELESTIAL EQUATOR AND ECLIPTIC
Below, scroll the sky map to the right and left to view the current circumstances along the Celestial Equator (aqua line) and the Ecliptic (red line). You will notice that the Ecliptic is plotted in line segments, as the sky map is a composite, built up right to left of several segments, each accurate. Remember: east and west appear reversed because you are looking up, not down.
Courtesy: Fourmilab Switzerland


Note that you may click on the name or symbol of any object in the above legend, which opens a separate page for that object. This will show the object centered and zoomed-in on a map of a smaller, more detailed portion of the sky.
You will quickly find the locations of the Sun, the Moon, the major planets and dwarf-planet Pluto in the constel- lations of the zodiac, i.e. the constellations in which the Ecliptic lies. The plane of Earth's orbit, the Ecliptic is generally regarded as the plane of the Solar System, and it is usually the most active part of the sky. With this map and a Larger More Detailed Version, which both open centered on the Vernal (March) Equinox ( ), you will be able to keep track of the long-term motions of the Sun, the Moon, the major planets and Pluto, in- cluding when they move past each other or past major stars. For a slightly different perspective on this part of the sky, also see our Sun's Apparent Motion along the Ecliptic and Sun's Location on the Ecliptic pages.
), you will be able to keep track of the long-term motions of the Sun, the Moon, the major planets and Pluto, in- cluding when they move past each other or past major stars. For a slightly different perspective on this part of the sky, also see our Sun's Apparent Motion along the Ecliptic and Sun's Location on the Ecliptic pages.
CURRENT SUN, MOON AND MAJOR PLANET
VIEWS AND CONDITIONS FROM EARTH
Distances, Apparent Sizes, Phases, Moon Locations
Sun
Moon
Mercury
Venus
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Current Relative "Apparent" Sizes
of the Major Planets from Earth
Current Locations of the Planets in their Orbits
Motion of Sun Simulator
Here is a map that purports to show Every Visible Star in the Night Sky, in One Map ![]() Very impressive!
Very impressive!
And don't forget to also check out the Current Sky.
CURRENT YEAR'S ELONGATIONS
Major Sky Objects 2021-2030
Greatest: Mercury ![]() Venus
Venus ![]()
NEXT TRANSITS: MERCURY & VENUS
Mercury: 2032 Nov 13
![]() Venus: 2117 Dec 11
Venus: 2117 Dec 11
Current Locations of Jupiter's Galilean Moons
EQUINOXES, SOLSTICES & THE
SUN'S APPARENT MOTION
THE MESSIER OBJECTS
 The Messier objects rank among the all-time favorites of avid sky viewers! This is because they can easily be viewed in small telescopes (as small as 4" aperature). They thus include some of the most famous sky objects, many of which are known even to non-sky-enthusiasts. M31, for example, is the famous Andromeda Galaxy and M42 is the Orion Nebula.
The Messier objects rank among the all-time favorites of avid sky viewers! This is because they can easily be viewed in small telescopes (as small as 4" aperature). They thus include some of the most famous sky objects, many of which are known even to non-sky-enthusiasts. M31, for example, is the famous Andromeda Galaxy and M42 is the Orion Nebula.
Here is a link to the SEDS site's excellent Interactive Messier Objects page. Clicking on each object's image leads you to loads of images and info, including its coordinates and diagrams to help you find it in the sky.
DEEP-SKY OBJECTS (DSO's)
The term "deep-sky objects" (DSO's) typically refers to celestial "groupings" or "formations" that are neither ordinary stellar systems nor members of any solar system. These include star clusters, nebulae and galaxies, and they offer sky viewers some of the most captivating observations possible. For example, the 110 Messier objects are all deep-sky objects. But there are also myriads of others!
The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars (abbreviated "NGC") and the Index Catalogue (abbreviated "IC") are two standard references that offer lists of thousands of deep-sky objects. (The Messier Objects are also included in the NGC.)
The SEDS site's Interactive NGC Catalog Online offers one of the best portals to information about deep-sky objects.
Wikipedia's New General Catalogue and IC Objects pages are also good sources of information about deep-sky objects.
Also check out our own Deep-Sky Objects page.
OBSERVING PROGRAMS
Okay, we know it; the Universe is a "biggggggg" place! So, at times, deciding which of the sky's innumerable marvels you want to observe can seem a bit daunting. Would you like some help? The Astronomical League has established some terrific Observing Programs to help you get the most out of your sky viewing.
MORE SKY-VIEWING AIDES
Mercury's and Venus's Sky Paths 2013–2014
Free SFA Observatory Full-Sky Star Charts PDF
VIEWING CONSIDERATIONS
ESTIMATING ANGULAR DISTANCES
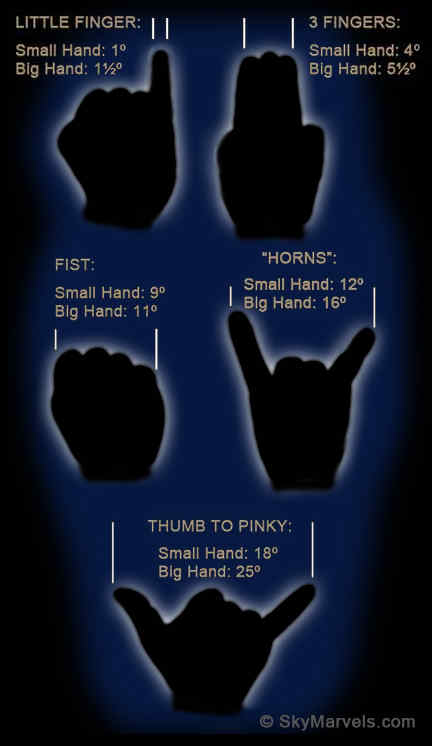
Since your hand is always "handy", you can use these rules of thumb (so to speak) to estimate how far apart objects appear in the sky. Views are of your hand held out with your arm fully extended.
Another very useful benchmark to remember is this: a U.S. penny held 43 inches from your eye subtends an angle of 1° (one degree).
PARALLAX
Parallax is the apparent displacement of a closer object relative to a farther object as we change the position from which we view them. Here's a nice little interactive that demonstrates Parallax.
Home Intro News Gallery Sky-Gifts Bonuses Tips
Learning Ctr Help Links Credits Legal Contact Us
© 2007-
by Gary M. Winter. All rights reserved.
Interested in political cartoons and humor?
Check out The HIPPLOMATS™.
SkyMarvels, Sky Marvels, SkyMarvels.com, SKY VIEWING!, Tonight's Sky! Current Sunsize vs Moonsize, Sky Maps!, Eclipses, Eclipse Calendar, Interactive Eclipse Seasons Calendar, Eclipse Seasons, Current Planet Positions!, Sky Viewing This Month!, Moonrise and Moonset!, Sunrise and Sunset! Aurora Forecasts! Aurora Borealis, Northern Lights, Aurora Australis, Southern Lights, Viewing Considerations, Twilight, Horizon Effect, celestia4all, celestiaforall, CELESTIA, astronomy, space, simulations, animations, downloadable astronomy posters, stars, planets, Inner Planets, Outer Planets, Inferior Planets, Superior Planets, moons, asteroids, comets, Oort Cloud, galaxy, galaxies, Milky Way, Andromeda, globular clusters, binaries, quasars, black holes, supermassive black holes, Deep-Sky Objects, DSO's, telescope, telescopes, planetarium, software, freestuff, satellites, add-ons, addons, scripts, eclipses, Solar Eclipses, Lunar Eclipses, Solar Eclipse Finder, Lunar Eclipse Finder, mutual eclipses, transits, occultations, Solar System, CELES-TOOLS, celeSTARrium, CELX, CELX programming, Freebies, Bonuses, multiple views, atronomical unit, light year, parsec, meteors, meteor showers, Perseids, Geminids, Leonids, barycenter, time, Time Zones, tides, alignments, conjunctions, oppositions, seasons, apogees, perigees, aphelion, perihelion, Earth, Luna, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Galilean Moons, Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto, Saturn, Titan, rings, Uranus, Neptune, Triton, E-MSpectrum, electromagnetic spectrum, astronaut, equinoxes, solstices, precession, rotation, spin, inclination, tilt, Ecliptic, orbits, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola
Moon's Position Over Earth
(to update, reload page)
Courtesy: Fourmilab Switzerland
Current Moon
![]()
![]()
Location in the Constel.
NASA's Daily Moon Guide
(to update, reload page)

 K E E P S A F E! It is never NEVER safe to
K E E P S A F E! It is never NEVER safe to
look directly at the real Sun with the naked
eye! Moreover, looking at it—even for an instant—
through a telescope, binoculars, camera or similar
instrument without adequate safeguards can cause
permanent blindness! NEVER DO IT! To learn how
you can safely "observe" the Sun, consult the pro-
fessionals at your local planetarium or observatory.
SKY VIEWING
SOLAR SYSTEM
THE SUN
MERCURY
VENUS
EARTH
THE MOON
MARS
JUPITER
SATURN
URANUS
NEPTUNE
SMALLER WORLDS
STELLAR OBJECTS
EXOPLANETS
DEEP-SKY OBJECTS
SCALE OF THE COSMOS
———————
SKY-FUN / SKY-GAMES
Donate safely with: PayPal
and receive one or more
Sky-Gifts. Your support is greatly appreciated!
NOTE: you do not need a PayPal account to donate.
CURRENT & UPCOMING
Earth's Mean Tilt Today
relative to the Sun
Aurora Forecast:
N Lights: (Aurora Borealis)
S Lights: (Aurora Australis)
Comets:
Visible in N Hemisphere
Visible in S Hemisphere
Moon-Planet Occultations:
Supermoons and Extreme Perigean Tides 2020-2022
Planet Conjunctions: List
Meteor Showers:

IMO:
Calendar
PDF
AMS:
Calendar
Major Shower Animations
Next Transits:
NASA's LATEST:
ISS (Int'l Space Station) Info:
Live ISS Stream Spot the Station
SDO (SOLAR DYNAMICS OBSERVATORY)
Sun Activity: Today's Vids
Sunspots may not see
any at Solar Min ![]()
Prominences
AIA 171 (gold)
AIA 193 (bronze)
AIA 1700 (pink)
Interactive Tool
ESA's LATEST
SKY-VIEWING
FUN FACTS
Though farther objects may be reported when viewing is exceptional, the Andromeda galaxy, M 31, is considered
to be the farthest object that can normally be seen by the naked eye! It is roughly 2½ million light-years away!
Estimates place the number of stars visible to the naked eye at about 6,000! That is over the entire 360° sky.
Apparent magnitude tells us how bright an object looks from Earth. A bit like golf, where a lower score is best, brighter sky objects have lower apparent magnitudes! For example, the Sun has an apparent magnitude of about -27 ("minus" 27). Contrast this with Pluto, which has an average apparent magnitude of about +15 ("plus" 15)!
The un-assisted human eye, also called the "naked eye", can typically distinguish sky objects whose apparent magnitudes are +6.5 or less. All observation of the sky was limited to this until the early 1600's, when the first telescopes were invented!
An 8" telescope can enable the viewing of objects with apparent magnitudes which exceed +14!
SKY VIEWING INTERACTIVES
Here are five awesome 3-D skymaps to aid your viewing:
D3 Celestial Starmap this is an awesome tool!
Moon Phaser an awesome interactive tool!
SKYMARVELS™
CELESTIA ADD-ONS