


Venus is a cloud-veiled world, whose thick atmosphere's "surface pressure" is over 90 times that of Earth's! (1.6.x) (1.4.1). Here is a view of Venus's surface beneath its clouds! (1.6.x) (1.4.1)
Venus, the second planet from the Sun, has the most circular orbit of
the major planets!
(1.6.x)
(1.4.1)
On Venus it "rains" sulfuric acid stronger than the acid found
in car batteries!

Venus exhibits an immense V-shaped
cloud structure, which girdles the planet! (1.6.x)
SURFACE VIEWS
Venus's surface is so hostile that no lander spacecraft has operated there for more than a few hours! So, few photos of this harsh surface exist.
Russian VENERA Spacecraft:
From The Planetary Society, here's a fascinating article. Every picture from Venus' surface, ever!
Here's a cool NASA artist's impression that shows
Here are NASA artist's con- cepts of the DaVinci Mission
Here is NASA's Proposed Venus Landsailer
![]()
VENUS ACTIVITIES
VIEW VENUS IN
BROAD DAYLIGHT
That's right, it can be done! Most people don't realize that Venus is often visible during the day, so you'll probably be the first in your group to view this brightest of the planets in broad daylight! Use the tips on this page to help you with your viewing.
MAKE A PAPER MODEL GLOBE OF VENUS
From the cool Solar System Scope site, download these paper globe templates for all the planets, the Sun and the Moon—including templates for both a cloud-covered and cloudless Venus! Make a Venus, half with clouds, half without! Then make the full Solar System!
CELES-TIPS
The following will help you enjoy this page's 1.6.x and 1.4.1 links that run events directly in CELESTIA. If you're new to the program, these tips will also help you learn to use it.
Are you unfamiliar with our 1.6.x and 1.4.1 links? For an explanation click here.
You'll find more information about many of CELESTIA's controls on our Learning Center page.
VENUS
View Venus in 3-D 3-D in Orbit
Current Views and Conditions from Earth
Current Location in the Constel. Skypath 2026
Current Location in Orbit
Current Year's Greatest Elongation ![]()
Next Transit Pair: 2117 Dec 10-11 2125 Dec 8
Physical Properties:
Equatorial Size: Compare in 3-D
Radius: 6,051.8 km

Diameter: 12,103.6 km
Diameter (Earth = 1): 0.949
Rotational Flattening: 0
Mass (Earth = 1): 0.815
Volume (Earth = 1): 0.857
Mean Density (Water = 1): 5.24
Mean Density (Earth = 1): 0.951
Surface Gravity (Earth = 1): 0.905
Surface Temperatures: average 462°C (863°F) ![]()
Axial Tilt: 177.36° ![]()
Where Poles Point ![]()
 Compared to the other
Compared to the other
major planets, Venus—
shown cloudless here— spins backwards (retro- grade) and quite slowly!
If viewed from "above"
the Solar System, its ro-
tation would appear to proceed "clockwise".
Rotation:
Direction: Retrograde
Period:
Synodic ("Day" in Earth solar* days): 116.75
Sidereal (Earth solar* days): 243.02
Note: Earth Day Lengths
Mean Solar: 24.0000 hours (24h00m00s)
Sidereal: 23.9345 hr (23h56m4.1s)
Albedo (geometric): 0.67 (highest of Major Planets)
Magnetic Field (Earth = 1): ~ 0.000015 (very weak)
NASA's Overview of Venus
NASA / JPL's Photojournal pages for Venus
Venus Surface:
Global Mosaic (26.4 km per pixel)
NASA's Venus Trek
Venus Atmosphere ![]()

While Venus's scorched
surface below rotates very slowly, its thick clouds sweep around the planet about every four to five Earth days!
Venus Structure:
Compared to Other Inner Planets
![]()

Spacecraft in 3-D:
Venera 7 ![]() 12-14
12-14 ![]() 15-16
15-16 ![]()
Vega 1 & 2 ![]()
![]()
Number of Moons: 0
Ring System: No
Planet Classifications:
Inner Planet (along with Mercury, Earth & Mars)
Terrestrial Planet (primarily Earth-like structure)
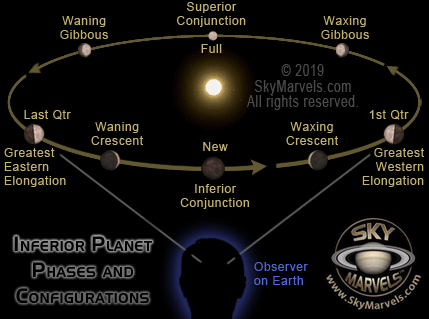
Inferior Planet (has smaller orbit than Earth and
exhibits a full range of phases)
Current Phase of Venus
Phases of the Inner Planets Video
Phases of Venus Sim Another
Configurations Sim (in Orbit Sizes box
select Earth and Venus)
No. of Greatest Elongations per Yr: 0, 1 or 2 ![]()
Orbit:
(1.6.x)
(1.4.1)
Period: 224.701 Earth solar* days
Distance from Sun:
Mean (Earth = 1 AU): 0.723 AU
Mean: 108,210,000 km
Perihelion: 107,480,000 km (0.718 AU)
Aphelion: 108,940,000 km (0.728 AU)
Velocity:
Mean: 126,072 km/hr
Min: 125,244 km/hr
Max: 126,936 km/hr
Eccentricity: 0.0067
Inclination to Ecliptic: 3.39°
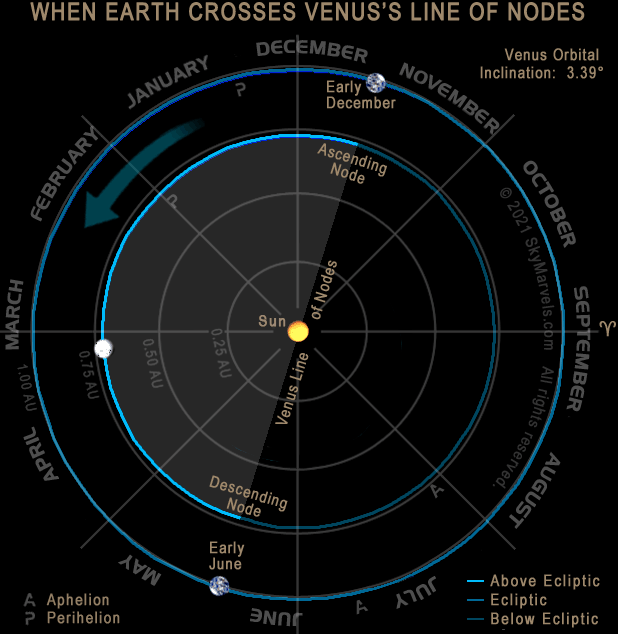
When Venus's Orbit Appears "Edge-On" from Earth
Transits (in front of the Sun):
Pattern: Pairs 8 Years Apart
Pairs Alternate by 121½ then 105½ Yrs
Last Pair: 2004 Jun 8; 2012 Jun 5-6
Last Pair: 2004 Jun 8 2012 Jun 5-6
Next Pair: 2117 Dec 10-11 2125 Dec 8
Currently all occur in June or December
Wikipedia's Transit of Venus page
NASA's Six-Millenium Catalog of Venus Transits
NASA Graphic of the 2004 and 2012 Transits
NASA 2012 June 5-6 Transit Page
NASA SDO's 2012 Venus Transit video
video credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Obs/Goddard Sp Flt Ctr

Let's see how CELESTIA depicts this event, the
last of its kind for over a hundred years (1.6.x).
Compare it to the video directly above.
Partial Information Source: NASA Fact Sheets
ADJECTIVES MEANING
"pertaining to Venus"
Venerean, Venusian
Cytherean (from Greek goddess, Cythera)
VENUS: Its Phases as an Inferior Planet
MERCURY'S & VENUS'S SKY PATHS 2013–2014
NASA/RASC Conceptual Mission to Venus
video credit: NASA/RASC
VENUS: Magellan Planet Flyovers/Radar Calibration Results
video credit: NASA/JPL
Here's a very nice Wikipedia page: List of Missions to Venus. Lots of good background info here!
Home Intro News Gallery Sky-Gifts Bonuses Tips
Learning Ctr Help Links Credits Legal Contact Us
© 2007-
by Gary M. Winter. All rights reserved.
Interested in political cartoons and humor?
Check out The HIPPLOMATS™.
SkyMarvels, Sky Marvels, SkyMarvels.com, Venus, View its Current Distance, Current Apparent Size, Current Phase, Current Position in Orbit and much more! celestia4all, celestiaforall, CELESTIA, astronomy, space, simulations, animations, downloadable astronomy posters, stars, planets, Inner Planets, Outer Planets, Inferior Planets, Superior Planets, moons, asteroids, comets, Oort Cloud, galaxy, galaxies, Milky Way, Andromeda, globular clusters, binaries, quasars, black holes, supermassive black holes, telescope, telescopes, planetarium, software, freestuff, satellites, add-ons, addons, scripts, eclipses, Solar Eclipses, Lunar Eclipses, Solar Eclipse Finder, Lunar Eclipse Finder, mutual eclipses, transits, occultations, Solar System, CELES-TOOLS, celeSTARrium, CELX, CELX programming, Freebies, multiple views, atronomical unit, light year, parsec, meteors, meteor showers, Perseids, Geminids, Leonids, barycenter, time, Time Zones, tides, alignments, conjunctions, oppositions, seasons, apogees, perigees, aphelion, perihelion, Earth, Luna, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Galilean Moons, Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto, Saturn, Titan, rings, Uranus, Neptune, Triton, E-MSpectrum, electromagnetic spectrum, astronaut, equinoxes, solstices, precession, rotation, spin, inclination, tilt, Ecliptic, orbits, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola

Donate safely with: PayPal
and receive one or more
Sky-Gifts. Your support is greatly appreciated!
NOTE: you do not need a PayPal account to donate.
SKY VIEWING
SOLAR SYSTEM
THE SUN
MERCURY
VENUS
EARTH
THE MOON
MARS
JUPITER
SATURN
URANUS
NEPTUNE
SMALLER WORLDS
STELLAR OBJECTS
EXOPLANETS
DEEP-SKY OBJECTS
SCALE OF THE COSMOS
———————
SKY-FUN / SKY-GAMES
VENUS FUN FACTS
When at its brightest, Venus can be seen in full daylight! But you have to know where to look for it.
To us here on Earth, Venus exhibits phases like those of the Moon! But, while lunar phases progress across the Moon from west to east (rel- ative to our sky directions), Venus's phases appear to progress "backwards", that is, from east to west!
The phases of Venus are not of as uniform in their dura- tion and timing as those of the Moon! As an Inferior Planet, Venus appears more than "half-illuminated" for a good bit more than half of its orbit!
Venus's atmosphere is so thick that its pressure at the planet's surface is close to that found half a mile deep in Earth's oceans!
Venus's rotation is so slow that the planet's day is longer than its year!
Venus spins backwards on its axis, compared to all of the other major planets!
Venus has the most circular orbit of the major planets!
Due to the size of its orbit, Venus can often provide "slingshot effect" gravity-assists for solar-orbit and interplanetary missions. Its gravity has already assisted at least four missions!
Volcanoes ![]() are constantly re-shaping Venus's surface! So it actually has relatively few visible impact craters!
are constantly re-shaping Venus's surface! So it actually has relatively few visible impact craters!
While it is harder for planets closer to the Sun to hold on to moons, Venus is at an ad- equate distance theoretically to do so. Why Venus has no moons is one of the planet's great mysteries.
VENUS INTERACTIVES
QUICK ACCESS LIST
Note: some links are echoed elsewhere on this page and may include descriptive text.
View Venus in 3-D: zoom and scroll this great interactive from SketchFab.
Links to interactive features that show Venus's orbit in 3-D can be found on our Solar System page
From UNL, this interactive shows How Venus Exhibits Phases as it and Earth orbit the Sun.
View Venus's configurations relative to the other planets with this awesome Planetary Configurations: Simulator.
SKYMARVELS™
VIDEOS FEATURING VENUS
Moon's Occultation of Venus 2010 May 16
Moon's Occultation of Venus 2010 Sep 11