










Sun's Position Over Earth
(to update, reload page)
Courtesy:
Fourmilab Switzerland
Explore the universe in stunningly realistic 3-D!
View Earth's Night Half
Day, Night & the Analemma
Earth Tilt, Sunrise & Sunset
Six Current Views of Earth
Current Global Cloud-Cover
Current Global Weather
Earth's 12-Month Heartbeat


UPCOMING
Comets:
Visible in N Hemisphere
Visible in S Hemisphere
Moon-Planet Occultations:
Supermoons & Extreme Perigean Tides 2020-2022
Planet Conjunctions: List
Meteor Showers:
IMO:
Calendar
PDF
AMS:
Calendar
Major Shower Animations
Launches & Landings:
Next Transits:
USEFUL ASTRO-WEBTOOLS
NASA:
Julian Date Converter
Coordinate Converter
Heasarc Tools
NEW HORIZONS:
Astronomical Lexicons:
NASA / JPL:
Basics of Space Flight
HubbleSite Glossary
Imagine the Universe!
NED (quite extensive)
ESA:
Glossary
Earth Online Glossary
List of Constellations (with pronunciations):
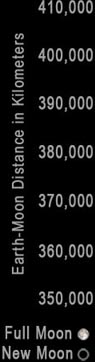
LUNAR APOGEES & PERIGEES
Lunar apogees & perigees show just how irregular the lunar orbit is. From 1500 to 2500 CE, the Moon's apogee averages about 405,400 km, varying from about 404,050 km to its extreme maximum of about 406,720 km. The lunar perigee is much more variable however, averaging close to 363,400 km while varying from about 370,350 km to its extreme minimum of about 356,370 km!
Extreme lunar apogees and perigees are caused mostly by the Sun's gravitational pull on the Moon, and they tend to happen in the winter months of the Northern Hemisphere. This is when Earth is near perihelion, i.e. closest (yes, closest!) to the Sun. Extreme apogees tend to happen when the Moon is New, since the Sun pulls it "away from" Earth. Extreme perigees in contrast tend to occur when the Moon is Full, as the Sun pulls it "toward" Earth. Forecasting these extremes can be important due to the Moon's influence on Earth's tides.
UTC: CELESTIA'S DISPLAY OF TIME
CELESTIA's clock displays Coordinated Universal Time, UTC. Click here for a brief explanation.
WHEN ARE EARTH & THE SUN CLOSEST?
When is Earth at perihelion, the point in its orbit closest to the Sun? Contrary to popular belief, this happens in the Northern Hemisphere's winter NOT summer! The winter season is not caused by Earth being farthest from the Sun, but rather by Earth's changing tilt in its orbit relative to the Sun!
In contemporary times Earth generally passes through perihelion between January 1 and January 6. In 2014, it occured on January 4 at 12 hour UT (Universal Time).
HIGHLIGHTS OF SOME
PAST SKY EVENTS
 Perseid Meteor Shower 2013 Aug
Perseid Meteor Shower 2013 Aug
 Geminid Meteor Shower 2012 Dec
Geminid Meteor Shower 2012 Dec
 Geminid Meteor Shower 2010 Dec
Geminid Meteor Shower 2010 Dec
 Perseid Meteor Shower 2010 Aug
Perseid Meteor Shower 2010 Aug
 Partial Lunar Eclipse 2010 Jun
Partial Lunar Eclipse 2010 Jun
Comet ISON 2013-2014:
View the The Path of Comet Ison from NASA.
Download a Paper Model of ISON's Orbit
SOME OLD-FORMAT
MONTHLY NEWS PAGES
2026 HIGHLIGHTS

 K E E P S A F E! It is never NEVER safe to
K E E P S A F E! It is never NEVER safe to
look directly at the real Sun with the naked
eye! Moreover, looking at it—even for an instant—
through a telescope, binoculars, camera or similar
instrument without adequate safeguards can cause
permanent blindness! NEVER DO IT! To learn how
you can safely "observe" the Sun, consult the pro-
fessionals at your local planetarium or observatory.
BEST PLANET CONJUNCTIONS:
 Feb 16 Saturn-Neptune (0.90° apart)
Feb 16 Saturn-Neptune (0.90° apart)
Mar 07 Venus-Neptune (0.07° apart)
Apr 13 Mars-Neptune (0.33° apart)
Apr 20 Mercury-Saturn (0.50° apart)
Apr 24 Venus-Uranus (0.77° apart)
Jul 04 Mars-Uranus (0.11° apart)
Aug 15 Jupiter-Mercury (0.55° apart)
MERCURY'S GREATEST ELONGATIONS:
Evening: Feb 19 18.1° E Mag: -0.2
Morning: Apr 03 27.8° W Mag: +0.5
Evening: Jun 15 24.5° E Mag: +0.7
Morning: Aug 02 19.5° W Mag: +0.4
Evening: Oct 12 25.2° E Mag: +0.2
Morning: Nov 20 19.6° W Mag: -0.3
2026 ECLIPSES:
Calendar
Annular Solar: Feb 17 Total Lunar: Mar 3
Total Solar: Aug 12 Partial Lunar: Aug 28
METEOR SHOWERS: Next 12 Months

MORE SKY EVENTS 2026
You can begin with this Sky Calendar from In-The-Sky , NASA's monthly Skywatching and The Sky Tonight . Also check out our Sky Viewing and Current Global Weather pages. And don't forget to verify your Sun- rise/set and Moonrise/set times from Time and Date .
2026: Perihelion & Aphelion Equinoxes & Solstices
MOON: ![]()
Current:
Orbital Position, Phase & Distance
Viewed from Earth: Appar. Size, Phase & Distance
Earth & Moon Viewed from Sun Interactive
Location in the Constellations
2026 Phase List with more Astronomical Events
2026 Best Moon-Planet Conjunctions
Moon Phase Interactives: #1 #2
Lunar Phase Simulator
MOON PHASES 2026
video credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
MAJOR MOON PHASES: ![]()
1.
![]() New MoonsNew Moons essentially rise and set with the Sun and reflect no sunlight toward Earth. So they do not impede Deep Sky Observing all night.
New MoonsNew Moons essentially rise and set with the Sun and reflect no sunlight toward Earth. So they do not impede Deep Sky Observing all night.
2.
![]() Waxing Crescent MoonsWaxing Crescent Moons generally
Waxing Crescent MoonsWaxing Crescent Moons generally
rise between sunrise and "local
noon". Setting between sunset
and "local midnight", they are up
and impede Deep Sky Observing
early in the evening.
3.
![]() 1st Qtr Moons1st Qtr Moons generally rise near "local noon". Setting near "local midnight", they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing for the first
1st Qtr Moons1st Qtr Moons generally rise near "local noon". Setting near "local midnight", they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing for the first
half of the night.
4.
![]() Waxing Gibbous MoonsWaxing Gibbous Moons generally
Waxing Gibbous MoonsWaxing Gibbous Moons generally
rise between "local noon" and sun-
set. Setting between "local midnight"
and sunrise, they are up and
impede Deep Sky Observing from
sunset through the early morning.
5.
![]() Full MoonsFull Moons generally rise near
Full MoonsFull Moons generally rise near
sunset, then set near sunrise. So
they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing all night long.
6.
![]() Waning Gibbous MoonsWaning Gibbous Moons generally
Waning Gibbous MoonsWaning Gibbous Moons generally
rise between sunset and "local
midnight". Setting between sunrise and "local noon", they are up and impede Deep Sky Observing in the
late evening through sunrise.
7.
![]() Last Qtr MoonsLast Qtr Moons generally rise near "local midnight" and set near "local noon", allowing Deep Sky Observing only during the first half of the night.
Last Qtr MoonsLast Qtr Moons generally rise near "local midnight" and set near "local noon", allowing Deep Sky Observing only during the first half of the night.
8.
![]() Waning Crescent MoonsWaning Crescent Moons generally
Waning Crescent MoonsWaning Crescent Moons generally
rise between "local midnight" and
sunrise. Setting between "local
noon" and sunset, they are up and
impede Deep Sky Observing only during the early morning.
2026 Lunar Perigees & Apogees
2020-2022 Supermoons & Extreme Perigean Tides
PRIOR AWESOME U.S. TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE:
2024 April 8 Maps Videos
SOLAR ECLIPSE QUICK REFERENCE MAPS
2001-2020 2021-2040 2041-2060
 KEEP SAFE! It is never safe to look directly at
KEEP SAFE! It is never safe to look directly at
the Sun with the naked eye! Moreover, looking at it—even for an instant—through either a telescope or binoculars without adequate safeguards can cause permanent blindness! NEVER DO IT! To learn how to safely "observe" the Sun and a Solar Eclipse, consult your local planetarium or observatory.
NASA's 5 Millenia of Eclipses: Solar Lunar
MAJOR LUNAR FEATURES
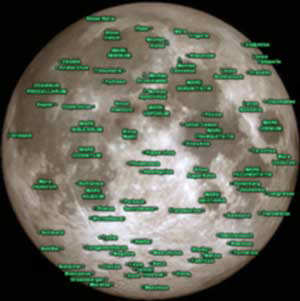
View the Moon's Features that are visible from Earth with binoculars or a low-power telescope.
Download NASA's Moon Observation Journal
View and download Moon maps to aid your viewing:
USAF Lunar Earthside Map (high-res)
NASA Apollo-Era Lunar Charts: Polar & Equatorial
Moon Landing Sites
EQUINOXES, SOLSTICES & THE
SUN'S APPARENT MOTION
EARTH FROM ABOVE ITS NORTH POLE
(at its Equinoxes)
CURRENT AURORA FORECASTS
Northern Lights: Aurora Borealis
Southern Lights: Aurora Australis
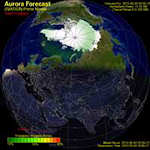
Image credit: NOAA / NWS Space Weather Prediction Center
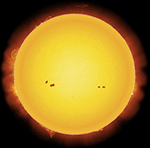 LATEST MAJOR SOLAR ACTIVITY
LATEST MAJOR SOLAR ACTIVITY
VISIBLE FROM EARTH
Sunspots Prominences, Flares, etc. Note: the SDO site has reported problems in early 2026.
 KEEP SAFE! It is never safe to look directly
KEEP SAFE! It is never safe to look directly
at the real Sun with the naked eye! Moreover, looking at it through a telescope or binoculars without adequate safeguards—even for an instant—can cause permanent blindness! NEVER DO IT! To learn how to safely "observe" the real Sun, consult the professionals at your local planetarium or observatory.
GET THE LATEST AWESOME SATELLITE
VIEWS OF THE SUN WITH "HELIOVIEWER"
HelioViewer might just be the best free solar astronomy tool on the web, giving you access to countless actual photos of the Sun from multiple satellites! "Time-step" through photos, and save and even make movies of what you find! This free web-tool is not to be missed.
And to help get you started, here's the direct link to the HelioViewer User Guide.
CELESTIAL EQUATOR AND ECLIPTIC
Courtesy: Fourmilab Switzerland


Above, scroll the sky map to the right and left to view the current circumstances along the Celestial Equator (aqua line) and the Ecliptic (red line). You will notice that the Ecliptic is plotted in line segments, as the sky map is a composite, built up right to left of several segments, each accurate. Remember: east and west appear reversed because you are looking up, not down.
Note that you may click on the name or symbol of any object in the above legend, which opens a separate page for that object. This will show the object centered and zoomed-in on a map of a smaller, more detailed portion of the sky.
You will quickly find the locations of the Sun, the Moon, the major planets and dwarf-planet Pluto in the constel- lations of the zodiac, i.e. the constellations in which the Ecliptic lies. The plane of Earth's orbit, the Ecliptic is generally regarded as the plane of the Solar System, and it is usually the most active part of the sky. With this map and a Larger More Detailed Version, which both open centered on the Vernal (March) Equinox ( ), you will be able to keep track of the long-term motions of the Sun, the Moon, the major planets and Pluto, in- cluding when they move past each other or past major stars. For a slightly different perspective on this part of the sky, also see our Sun's Apparent Motion along the Ecliptic and Sun's Location on the Ecliptic pages.
), you will be able to keep track of the long-term motions of the Sun, the Moon, the major planets and Pluto, in- cluding when they move past each other or past major stars. For a slightly different perspective on this part of the sky, also see our Sun's Apparent Motion along the Ecliptic and Sun's Location on the Ecliptic pages.
And don't forget to also check out the Current Sky for a more complete look at the overall sky.
CURRENT PLANET LOCATIONS IN ORBIT
SOLAR SYSTEM IN INTERACTIVE 3-D
The following all open showing current Solar System conditions—with views that you can rotate and zoom in 3-D!
These open with the Vernal (March) Equinox ( ) in the "3 o'clock" direction":
) in the "3 o'clock" direction":
NASA/JPL Orrery The Sky-Live jsOrrery
This one opens with the Vernal (March) Equinox
( ) in the "9 o'clock" direction":
) in the "9 o'clock" direction":
CURRENT SUN, MOON AND MAJOR PLANET
VIEWS AND CONDITIONS FROM EARTH
Distances, Apparent Sizes, Phases, Moon Locations
Sun
Moon
Mercury
Venus
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Current Relative "Apparent" Sizes
of the Major Planets from Earth
Current Locations of Jupiter's Galilean Moons
CURRENT YEAR'S ELONGATIONS
Major Sky Objects 2021-2030
Greatest: Mercury ![]() Venus
Venus ![]()
NEXT TRANSITS: MERCURY & VENUS
Mercury: 2032 Nov 13
![]() Venus: 2117 Dec 11
Venus: 2117 Dec 11
MERCURY'S & VENUS'S SKY PATHS 2013–2014
MERCURY MESSENGER status (completed mission with impact on Mercury as expected 2015 Apr 30)
View NASA's awesome Mars Exploration site.
MARS Weather: Curiosity
SATURN CASSINI MISSION: The Grand Finale
CLIMATIC VS. ASTRONOMICAL SEASONS
Most school children know that the climatic seasons of the two hemispheres are the reverse of each other's. For example, when it is Summer in the Northern Hemisphere, climatically-speaking it is Winter in the Southern Hemisphere.
Nonetheless the "astronomical" seasons, as well as their respective equinoxes and solstices, have always traditionally been named for the "climatic" seasons of the Northern Hemisphere—no doubt because roughly 90% of the human population lives north of Earth's equator! So the Summer Solstice, for instance, is the solstice in June at the beginning of the Northern Hemisphere's summer, etc.
Unfortunately, this traditional naming convention does create a potential ambiguity. For example, for Southern Hemisphere astronomers the "traditional" Summer Solstice occurs at the start of their climatic Winter!
This is why we often now see the less traditional (though slightly less recognizable) terms: March Equinox, June Solstice, September Equinox and December Solstice. Because these terms are more precise, they are increasingly becoming accepted as the best ways to refer to the equinoxes and solstices.
This shows Earth's snow and ice cover through the seasons Earth's 12-Month Heartbeat
HOW LONG IS EACH SEASON?
Since their beginnings and ends are explicitly defined by the Sun's arrival at the equinoxes and the solstices in our sky, Earth's astronomical seasons have precise durations. Moreover, though the equinoxes and solstices are equally spaced at 90-degree intervals around the Celestial Sphere, the astronomical seasons are not of equal length! This is because Earth's changing velocity in its elliptical orbit makes the Sun appear to arrive a little early at parts of the Celestial Sphere, and a little late at others. For the Northern Hemisphere the lengths of the astronomical seasons are very close to the following:
Spring: 92 3/4 days
Summer: 93 2/3 days
Autumn: 89 5/6 days
Winter: 89 days.
Of course, in the Southern Hemisphere the lengths of the "Astronomical" Seasons are the reverse of the ones listed above.
HALF OF EARTH IN SUNLIGHT & DARKNESS
During your voyages in CELESTIA, would you like to be able to position yourself directly over the center of the half of Earth in sunlight or the half in darkness at any time this month? On our Tips page, you'll find that it's quite easy to do so! If you're any kind of sky watcher at all, you probably know just how helpful this can be!
Home Intro News Gallery Sky-Gifts Bonuses Tips
Learning Ctr Help Links Credits Legal Contact Us
© 2007-
by Gary M. Winter. All rights reserved.
Interested in political cartoons and humor?
Check out The HIPPLOMATS™.
Astronomy Interactives. Current Sunsize vs Moonsize, SUN and MOON Current Apparent Sizes, Current Geocentric Apparent Sizes of the Sun and Moon. SkyMarvels: Your Key to the Sky and the Universe! SkyMarvels, Sky Marvels, SkyMarvels.com, SkyMarvels NEWS, SKY EVENTS NEWS, SKY NEWS, SKY EVENTS, TODAY'S LOCAL CLOUD COVER, THE SUN'S CURRENT POSITION OVER EARTH, THE MOON'S CURRENT POSITION OVER EARTH, CURRENT MOON PHASE, Current Planet Positions, Current Planet Locations, Eclipses, Eclipse Calendar, Interactive Eclipse Seasons Calendar, Eclipse Seasons, Aurora Forecast, Aurora Borealis, Northern Lights, Aurora Australis, Southern Lights, Supermoons & Extreme Perigean Tides, celestia4all, celestiaforall, CELESTIA, astronomy, space, simulations, animations, downloadable astronomy posters, stars, planets, Inner Planets, Outer Planets, Inferior Planets, Superior Planets, moons, asteroids, comets, Oort Cloud, galaxy, galaxies, Milky Way, Andromeda, globular clusters, binaries, quasars, black holes, supermassive black holes, telescope, telescopes, planetarium, software, freestuff, satellites, add-ons, addons, scripts, eclipses, Solar Eclipses, Lunar Eclipses, Solar Eclipse Finder, Lunar Eclipse Finder, mutual eclipses, transits, occultations, Solar System, CELES-TOOLS, celeSTARrium, CELX, CELX programming, Freebies, multiple views, atronomical unit, light year, parsec, meteors, meteor showers, Perseids, Geminids, Leonids, barycenter, time, Time Zones, tides, alignments, conjunctions, oppositions, seasons, apogees, perigees, aphelion, perihelion, Earth, Luna, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Galilean Moons, Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto, Saturn, Titan, rings, Uranus, Neptune, Triton, E-MSpectrum, electromagnetic spectrum, astronaut, equinoxes, solstices, precession, rotation, spin, inclination, tilt, Ecliptic, orbits, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola, USGS Daily Earthquake Map
Moon's Position Over Earth
(to update, reload page)
Courtesy: Fourmilab Switzerland
Current Moon
![]()
![]()
Location in the Constell.
NASA's Daily Moon Guide
(to update, reload page)
Earth's Mean Tilt Today
relative to the Sun
Donate safely with: PayPal
and receive one or more
Sky-Gifts. Your support is greatly appreciated!
NOTE: you do not need a PayPal account to donate.
SKY VIEWING
SOLAR SYSTEM
THE SUN
MERCURY
VENUS
EARTH
THE MOON
MARS
JUPITER
SATURN
URANUS
NEPTUNE
SMALLER WORLDS
STELLAR OBJECTS
EXOPLANETS
DEEP-SKY OBJECTS
SCALE OF THE COSMOS
———————
SKY-FUN / SKY-GAMES
ALL THE LATEST
![]() Current Solar System
Current Solar System
In 3-D! ![]() Top View
Top View
USGS's LATEST
NASA's LATEST
Exoplanet Counts:
HUBBLE Space Telescope:
Latest
News
Daily Report
News Release Archive
ISS (Int'l Space Station):
Live ISS Stream
Spot the Station
MARS 2020 Mission: Perse- verance Rover
MARS SPIRIT and OPPORTUNITY Locations
MERCURY MESSENGER mission ended with planned Mercury impact 2015 Apr 30
Near-Earth Object news
NEO Close Approaches
Fireball & Bolide Map
SDO (SOLAR DYNAMICS OBSERVATORY) Location
Sun Activity: Today's Vids
Sunspots may not see
any at Solar Min ![]()
Prominences
AIA 171 (gold)
AIA 193 (bronze)
AIA 1700 (pink)
Interactive Tool
VOYAGER 1 & 2:
ESA's LATEST
Where Is BepiColombo?
Wikipedia page
Where Is Solar Orbiter?
Wikipedia page
USNO's LATEST
MISCELLANEOUS
OBSERVATORIES
For the latest info go to the Observatories Listing on our Links page.
NOAA's LATEST
For more Climate Info, check out this nice interactive tool: NASA's Eyes on the Earth.
SPACE AGENCY NEWS
ESA News (search or scroll down)
SOLAR ANALEMMA
The Sun's Signature
The Sun's Current Position on the Analemma